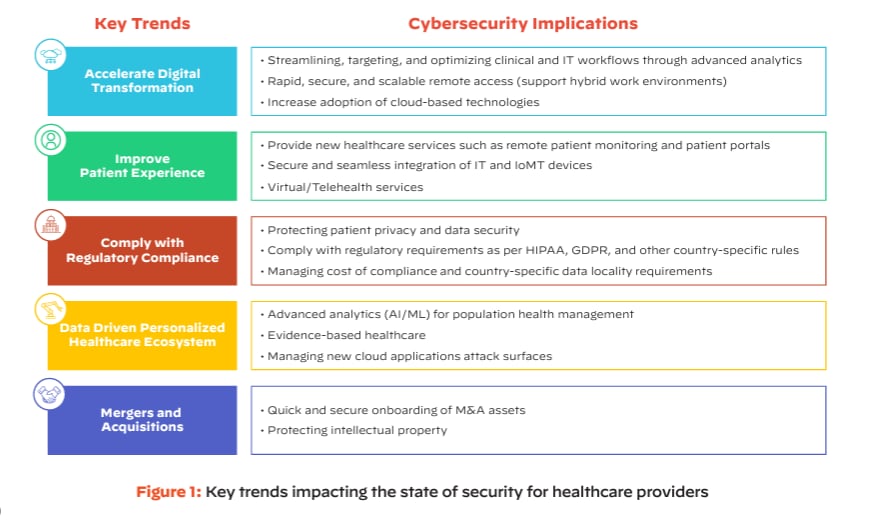
Partner POV | AI Provides an Rx for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
In this article
This article was written by Tapan Mehta, Global Leader, Healthcare Strategy and Solutions, Palo Alto Networks, and Dena De Angelo Content Marketing Manager at Palo Alto Networks.
As cyberthreats evolve and proliferate, healthcare organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to embrace artificial intelligence (AI) in their cybersecurity efforts. This can be especially difficult due to the inherent challenges of integrating new technologies into their complex and often legacy-laden environments.
And, as AI continues to evolve, its impact on healthcare cybersecurity is becoming increasingly significant. To explore this critical intersection, we spoke with Tapan Mehta, Healthcare and Pharma Life Sciences Executive, Strategy and GTM, about the challenges, opportunities and future of AI in protecting healthcare infrastructure and data.
The Current State of AI in Healthcare Security
While AI has made substantial inroads in medical diagnostics and treatment, its application in healthcare cybersecurity is still in its nascent stages. However, the potential for AI in healthcare security is immense. Mehta notes:
"AI is a perfect match for ingesting [internet of things] IoT data, as the devices generate such huge amounts of data that we couldn't access before, or we couldn't access in real time. This capability is crucial as healthcare organizations face an ever-expanding attack surface. Additional examples of where AI is being used include medical imaging analysis, predictive analytics for population health management, and virtual health assistants and chatbots."
Unique Challenges in Healthcare Cybersecurity
The healthcare industry faces unique cybersecurity challenges stemming from its traditionally cautious approach to new technology adoption, which is coupled with the highly sensitive nature of its data. The sector has been slower to embrace cutting-edge technologies compared to other industries. It still grapples with a complex mix of legacy systems, gradual digital transformation and the integration of connected devices (medical, OT and IoT). This cautious, often piecemeal approach to modernization, combined with the critical nature of patient data and care delivery, creates a distinctive and vulnerable cybersecurity landscape. Mehta comments further:
"Unlike other industries, the healthcare industry is usually not at the forefront of cutting-edge technology because of the nature of the industry, because of patient privacy and data security. There's this 'wait-and-watch' mindset. Healthcare organizations want to see what other industries are doing and how they're adopting AI.
So when we think about AI in healthcare, I would say it is very much in its early infancy. And to use the baseball analogy, I would say it's like inning one or two of this journey in the healthcare space. And it again centers back to regulatory requirements as well, including patient privacy and data security and everything related to that."
Smart medical devices often lack robust privacy controls and security features, while many medical IoT devices transmit unencrypted data. The mixing of IoT/OT and IT assets on healthcare networks, combined with the prevalence of outdated operating systems on medical devices, creates a complex and vulnerable environment. To that end, Mehta explains how the modern care model is evolving, further expanding the resultant threat landscape:
"It is no longer confined to the four walls of the hospital, which I'm going back to five, six years ago. That's how you typically receive care. You have to go to the hospital, but that care model has shifted dramatically, moving from an acute care setting to an ambulatory care setting or outpatient setting to what we call a hospital-at-home or home setting.
In other words, providing a very high level of quality care regardless of where the patient is located. And you have a scenario where that model has transcended the hospital's walls. It opens up the exposure area or the attack surface."
The proliferation of internet-connected medical devices and mobile apps handling protected health information (PHI) and personally identifiable information (PII), without proper safeguards, further compounds these risks.
Moreover, the healthcare sector's reliance on legacy systems, many of which are no longer supported by manufacturers, introduces persistent vulnerabilities. These outdated systems cannot receive critical security updates, leaving healthcare networks exposed to evolving cyberthreats. This combination of factors – rapid technological adoption, inadequate security measures and legacy system vulnerabilities – makes healthcare organizations particularly attractive targets for cybercriminals, underscoring the critical need for robust, AI-driven cybersecurity solutions in this sector.
Mehta emphasizes the gravity of the situation: "It's no longer a question of if a healthcare organization will be targeted, it's a question of when they will be targeted." This reality underscores the urgent need for robust AI-powered security solutions in healthcare.
How AI Is Transforming Healthcare Cybersecurity
Despite being in its early stages, AI is already making significant contributions to healthcare cybersecurity:
Threat Detection – AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyberthreat. This capability is particularly valuable in detecting sophisticated attacks that might evade traditional security measures.
Automated Response – AI can help automate initial containment actions when a threat is detected, significantly reducing response times. Mehta explains, "AI is really, really good at scaling up a solution to these billions of IoT devices, which is very hard for a human being to do."
Predictive Analytics – By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI can help predict and prevent potential security breaches before they occur.
Data Enrichment – AI can rapidly process and correlate data from various sources, including threat intelligence feeds, providing security analysts with enriched, contextual information to make more informed decisions.
Anomaly Detection in IoT/OT Devices – Given the large number of IoT devices in healthcare settings, AI can monitor device behavior patterns and quickly identify unusual activities that may indicate a compromise.
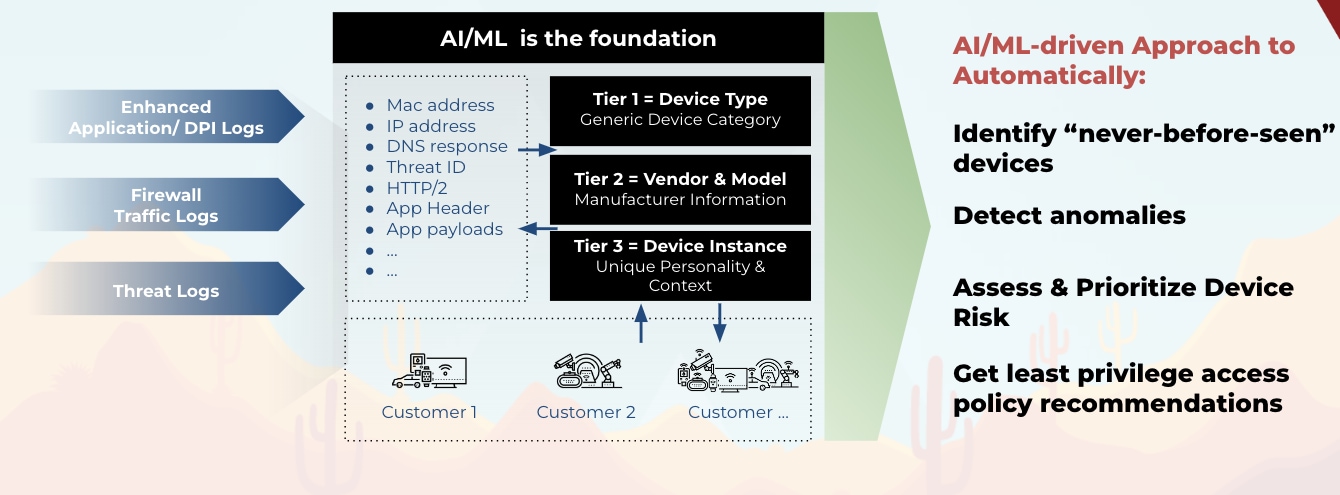
Natural Language Processing for Threat Intelligence – AI can analyze unstructured data from various sources to identify emerging threats specific to the healthcare sector.
Adaptive Security Policies – AI can continuously learn from new data and adjust security policies in real-time, ensuring that defenses evolve alongside new threats.
Behavioral Analysis – AI can establish baselines of normal user and system behaviors, flagging deviations that might indicate insider threats or compromised accounts.
Automated Vulnerability Management – AI can prioritize patching and remediation efforts by assessing the criticality of vulnerabilities in the context of the healthcare organization's specific environment and threat landscape.
Challenges in Implementing AI for Healthcare Cybersecurity
While AI holds great promise, its implementation in healthcare cybersecurity is not without significant challenges. The unique nature of healthcare cybersecurity creates a complex threat landscape for AI adoption:
Regulatory Compliance – Healthcare organizations must navigate complex regulations, such as HIPAA and GDPR, when implementing AI solutions. Mehta notes, "We're kind of flying the plane and fixing it, if you may, as we're flying that plane," referring to the evolving regulatory landscape around AI in healthcare.
Data Quality and Bias – AI models are only as good as the data they're trained on. Ensuring high-quality, unbiased data is crucial for effective AI-powered security solutions. In healthcare, where data can be highly variable and context-dependent, this challenge is particularly acute. Biased or incomplete datasets could lead to AI systems that are less effective for certain patient populations or types of healthcare facilities. This is particularly true as healthcare organizations continue to consider the usage of LLMs as part of their clinical and operational workflows.
Skills Gap – Mehta points out, "Healthcare organizations don't necessarily have the bench for this level of talent. Where cybersecurity is a very specific skill set that you need, if you're trying to layer that with AI, that pool gets even narrower." This shortage of professionals with both healthcare domain knowledge and AI expertise can significantly hinder the implementation and ongoing management of AI-driven security systems.
Integration with Legacy Systems – Many healthcare organizations rely on legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern AI technologies. Integrating AI solutions with these older systems without disrupting critical healthcare services presents a significant technical challenge.
Ethical Considerations – The use of AI in healthcare raises unique ethical concerns, particularly around patient privacy and data use.
Cost and Resource Allocation – Implementing AI solutions can be expensive, requiring significant upfront investment in technology and training. For many healthcare organizations operating on tight budgets, justifying these costs can be challenging.
Transparency and Explainability – In healthcare, where decisions can have life-or-death consequences, the "black box" nature of some AI algorithms poses a challenge. Ensuring that AI-driven security decisions are transparent and explainable is crucial for building trust and meeting potential regulatory requirements.
The Future of AI in Healthcare Cybersecurity
Looking ahead, Mehta envisions a future where AI plays an increasingly critical role in healthcare cybersecurity. He predicts, "Moving forward, I do see there is going to be further integration and leverage of AI for IoT. More scalable, more automation, more intelligent and faster identification and detection."
However, he also emphasizes the importance of human oversight:
"For example, when a medical device or system is hacked, not only can we lose sensitive information, but also it can impact the operation, which can mean life or death in the cases of healthcare and critical infrastructure. Therefore, the accuracy of AI is extremely crucial."
What Healthcare Needs from AI
Mehta's insights underscore the need for a balanced approach that leverages AI's capabilities while maintaining human expertise and oversight. As we move forward, healthcare organizations must invest in AI-powered security solutions, develop the necessary talent, and stay ahead of evolving regulations to protect sensitive patient data effectively.
As Mehta concludes:

